

The arrangement directly affects the sequence of the Periodic Table of Elements, the orbital shapes and the quantum leaps of the electron to various. The arrangement of these nucleons, in particular protons, is considered in this section and the section on orbital shapes. The nucleus of an atom occupies nearly 10-14 times the volume of the atom but contains 99.99 of the atomic mass. Rutherford’s scattering of alpha particles experiment revealed that the nucleus of an atom contains the majority of the atom’s mass. Counting the number of protons and neutrons tells scientists about the total mass of an atom. Given that these particles make up atoms, they are often referred to as subatomic. The atom’s nucleus is composed of nucleons ( protons and neutrons ). The nucleus of an atom is the central region of an atom that contains the majority of its mass. You have already learned that the mass of an electron is very, very small compared to the mass of either a proton or a neutron (like the mass of a penny compared to the mass of a bowling ball).
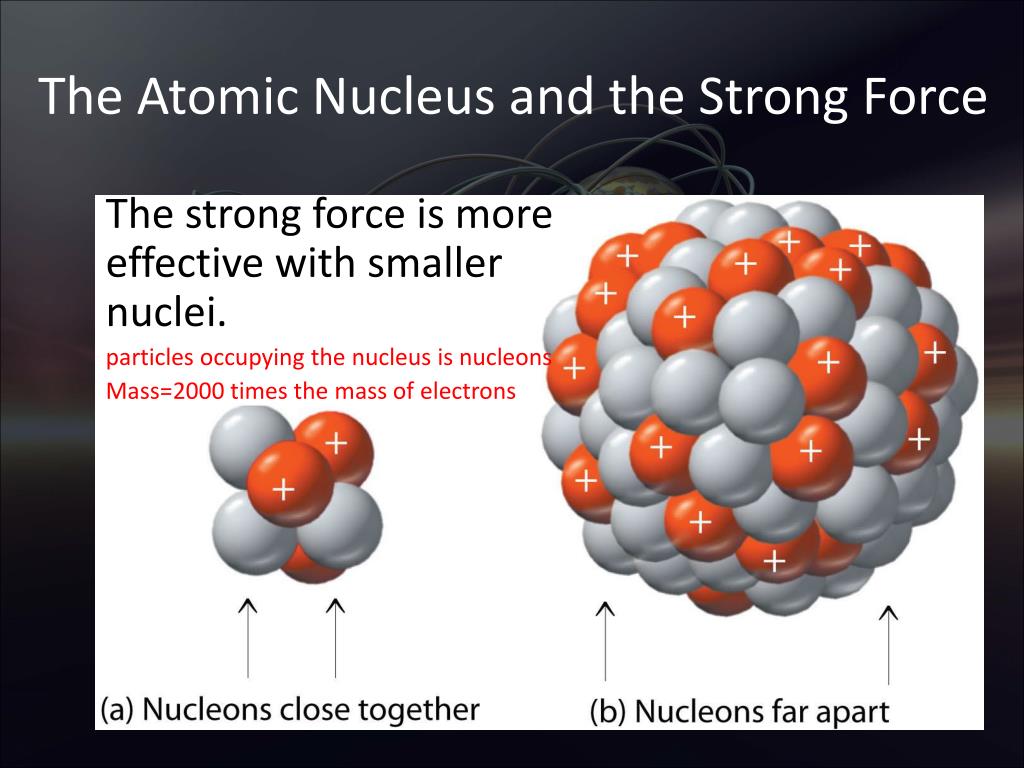
Surprisingly, the neutrons and protons in the nucleus move to a large extent in orbitals as though their wave functions were independent of one another.
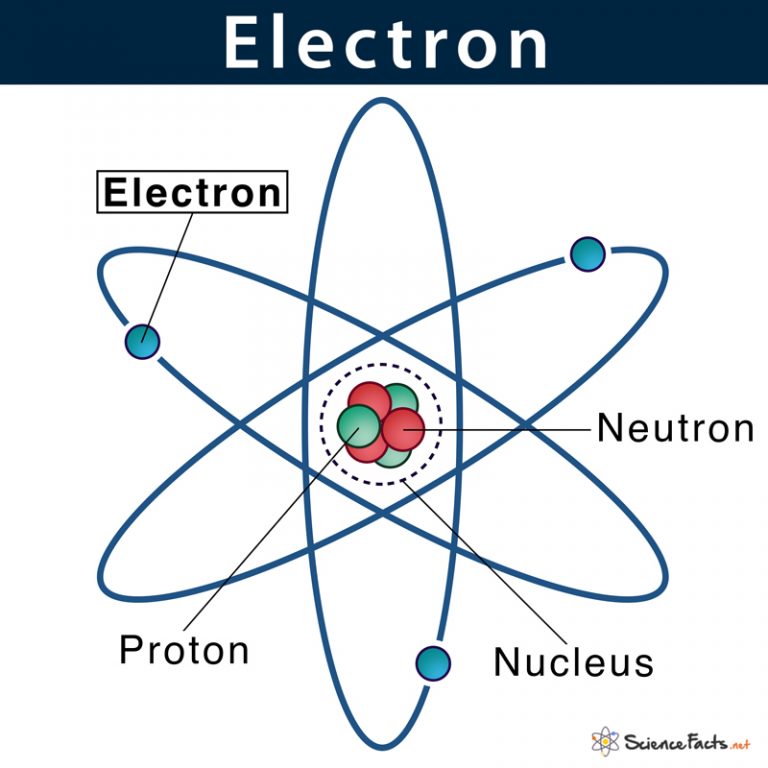
The mass of an atom depends on the number of protons and neutrons. Almost all nuclear phenomena can be understood in terms of a nucleus composed of neutrons and protons. Why do you think that the "mass number" includes protons and neutrons, but not electrons? You know that most of the mass of an atom is concentrated in its nucleus. For example, some helium atoms have three neutrons instead of two (these are called isotopes and are discussed in detail later on) The nucleus is surrounded by electrons that are negatively charged. In an atom, the nucleus accounts for nearly all of the total mass of the atom. Because the number of neutrons can vary for a given element, the mass numbers of different atoms of an element may also vary. An atom is made up of a positively charged, dense, and extremely small nucleus, which contains protons and neutrons, among other elements. Atoms with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons are called isotopes. However, some helium atoms have more or less than two neutrons.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
